Sharing and permissions
1. User management and permissions
Users in KAWA have a global profile that applies across all workspaces and some workspace related permissions.
1.1 Authentication
a. KAWA internal authentication
KAWA can be configured to authenticate users without relying on SSO. In this mode, administrators can either choose to let people create accounts using email activation codes or to manage the user accounts themselves through KAWA’s Python API.
KAWA will store the user’s unique identifiers (must be the email address if people are making use of email activation), their first and last names, and their secure password hashes.
When using KAWA internal authentication mechanism, the following page will be shown to users:
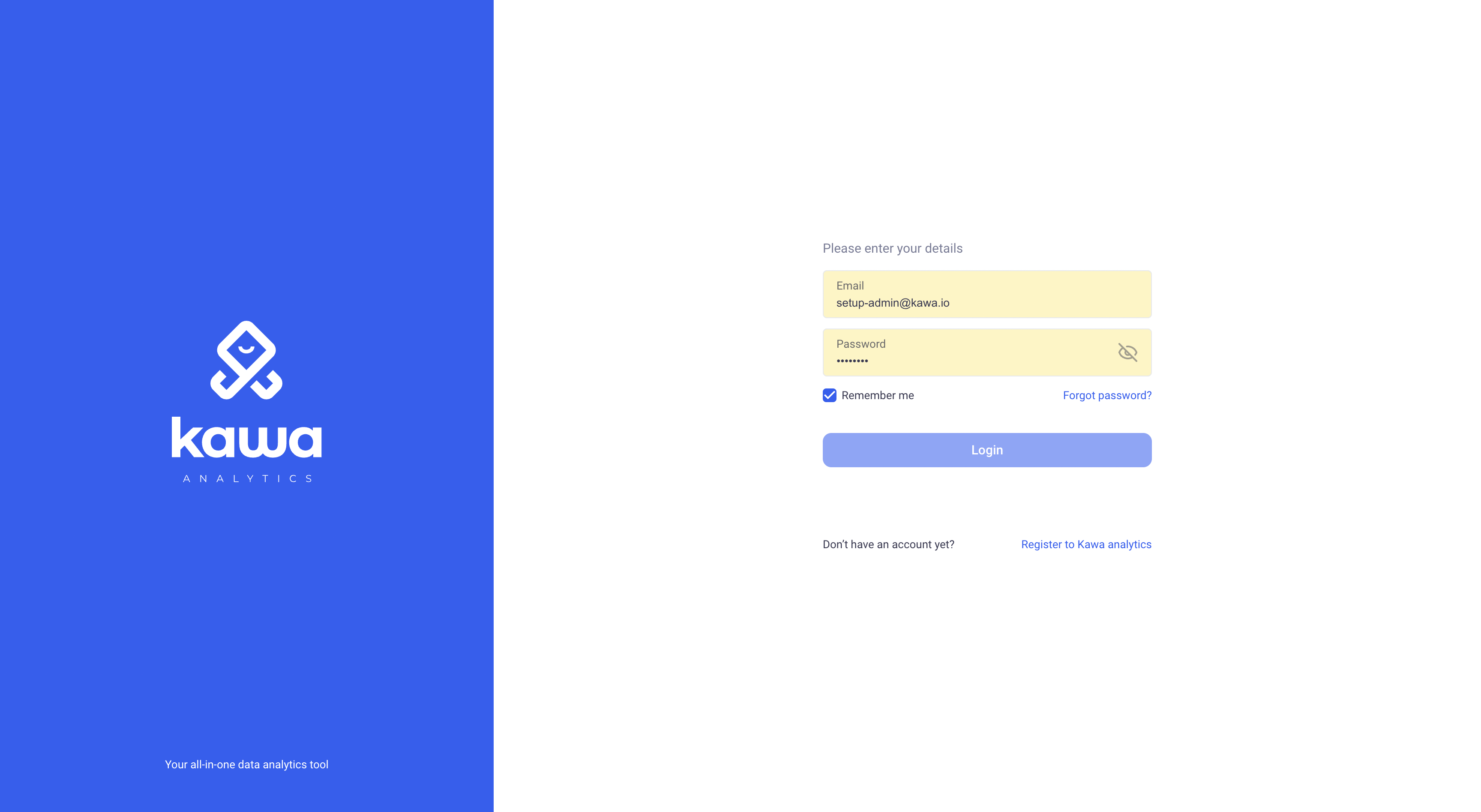
Important: Note that the “Register in KAWA Analytics” section can be turned off if you do not wish users to sign up by themselves. The feature flag name is:
user-sign-up.
Important: If you want to allow users to sign up, you need to configure SMTP support
b. Using external IDPs and SSO
When configured to work with SSO, KAWA will automatically create users in its database when new authenticated users will connect.
Open ID Connect: KAWA is compatible with OIDC to authenticate users. It can be integrated with providers such as OKTA, AWS Cognito, Auth0, Azure Active Directory, etc…
Kerberos SSO: Kawa can be configured to integrate with Kerberos to authenticate users.
HTTP Header-based Authentication: Users can be authenticated with HTTP Header based authentication. In that setup, the user information will be extracted from the incoming HTTP requests.
c. Using API Keys
KAWA provides a mechanism to allow users to generate API keys in order to authenticate. This is mainly used to work with KAWA’s Python API.
1.2 Application wide profile
Application wide profiles are configured through KYWY, KAWA’s python client.
Please refer to this repository: https://github.com/kawa-analytics/kywy-documentation which contains all the details and examples regarding the usage of this library.
a. The user roles
There are 3 global roles in KAWA. Each user has one role that is valid for the entire application.
Each time a new user is added in KAWA, they will get the REGULAR USER role.
ADMINISTRATORS
Administrators can access all the admin functionalities of the platform. They can create, delete, activate, deactivate users. They can also modify user passwords and change the global roles of other users.
Administrators can also access all workspaces and all assets in all of the workspaces without restrictions.
They can access all data bypassing all the row level and column level security.
Warning: Typically, very few admin accounts should be created. They should be reserved for IT, global support and maintenance.
SETUP ADMINISTRATORS
There is only one such user for the entire KAWA platform. This user has all the privileges of ADMINISTRATORS. It can never be disabled, deleted or switched to another user role.
REGULAR USERS
Most of the users should have this role. It allows them to benefit from all the features of the platform.
b. The restricted data source types
There are 7 data source types in KAWA:
-
USER FILES: To create data sources of that type, users can upload CSV files from the GUI.
-
EXTERNAL SYSTEMS: This type of data source is created by connecting to an external system directly from the GUI: Database, API, etc…
-
KYWY (Python client): This corresponds to data sources created from the Python client using the data loader.
-
LIVE CONNECT: Live connections are created by querying tables or views that are stored in the main data warehouse, without ETL or synchronization.
-
PYTHON ETL: This type of data source is created by scheduling a Python script decorated by the
@kawa_tooldecorator. -
FROM SCRATCH: This allows users to create data sources directly in the GUI and edit the values manually, like Excel.
-
TRANSFORMATIONS: Those are created by materializing existing views into new warehouse tables.
Each user (Regular users) can only create data sources of a type that was not explicitly restricted by administrators.
This allows administrators to control what the various users can load into the platform.
In the GUI, when users create a data source, the types they are allowed to work with are shown here:
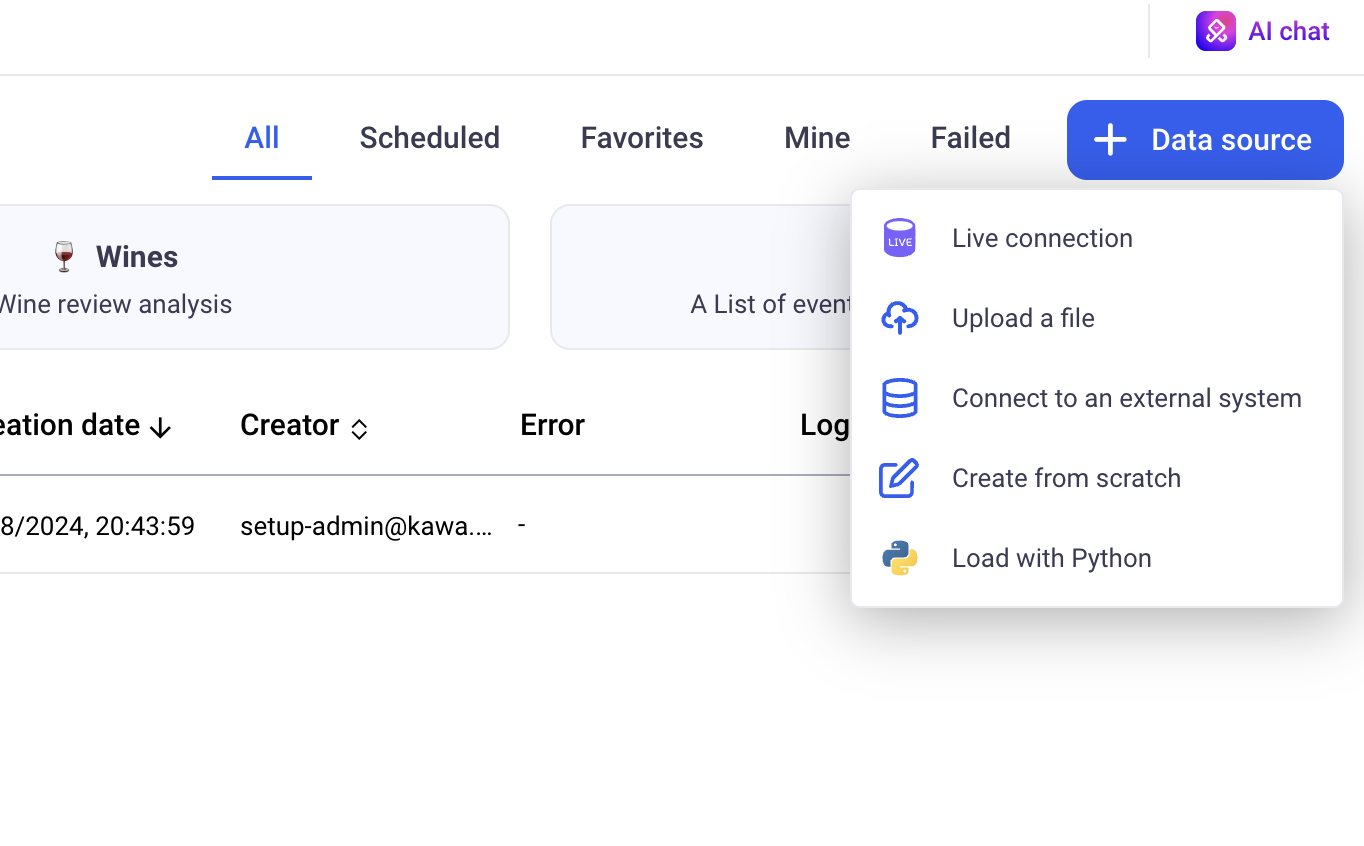
Important: by default, users will not have access to the LIVE CONNECT data type.
c. The overall permissions
Overall permissions are a list of features that individual users have access to. For example, to benefit from all the Generative AI features, the permission: GENERATIVE_AI must be granted. This grant will apply to the entire KAWA platform.
1.3 Workspace permissions
Each workspace functions as a separate isolated tenant. See definitions in Terminology section.
In order to access a given workspace, a user must be explicitly invited in it. A workspace can also be configured as public. If that is the case, all the registered users in the platform can access it without restriction.
In each workspace, users benefit from a set of permissions:
Sharing permissions:
- Share Sheets and Views
- Share Data Sources
- Share Dashboards
- Share Applications
- Share Knowledge
Misc:
- Access and manage Python scripts
- Run Python scripts
- Manage directories
Data access permissions:
Warning: Reserved to administrators of the workspace
- Manage row level and column level security
- Access restricted data and restricted data providers
Workspace administrative permissions:
Warning: Reserved to administrators of the workspace
- Edit workspace settings
- Manage workspace members
Workspace permissions are handled directly on the GUI, from the settings section (cog icon at the bottom left)
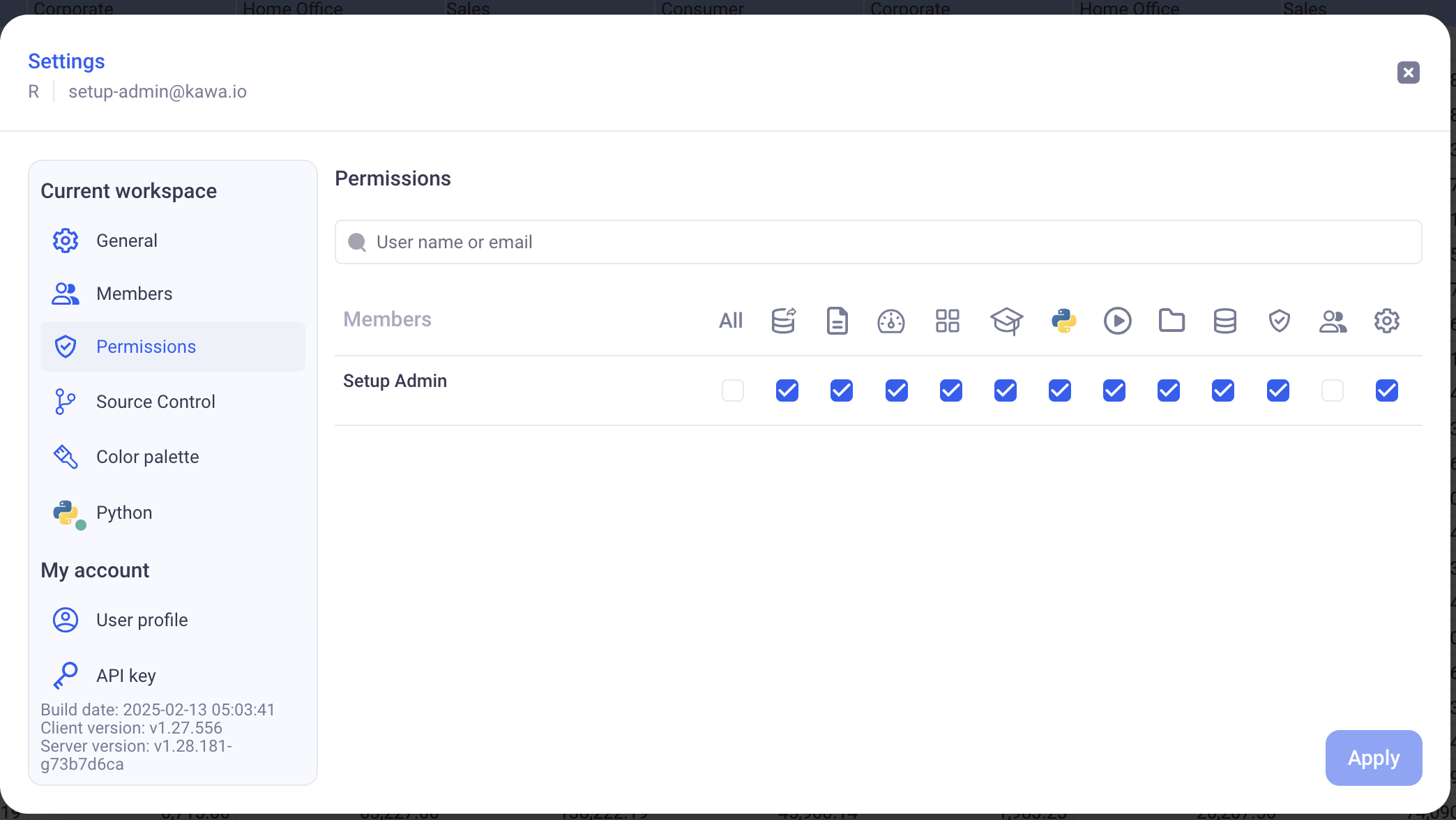
Warning: Administrative and data access permissions give users ability to directly or indirectly access all data. Those permissions should be reserved to workspace administrators only.
Warning: Application wide Administrators will benefit from ALL those permissions by default.
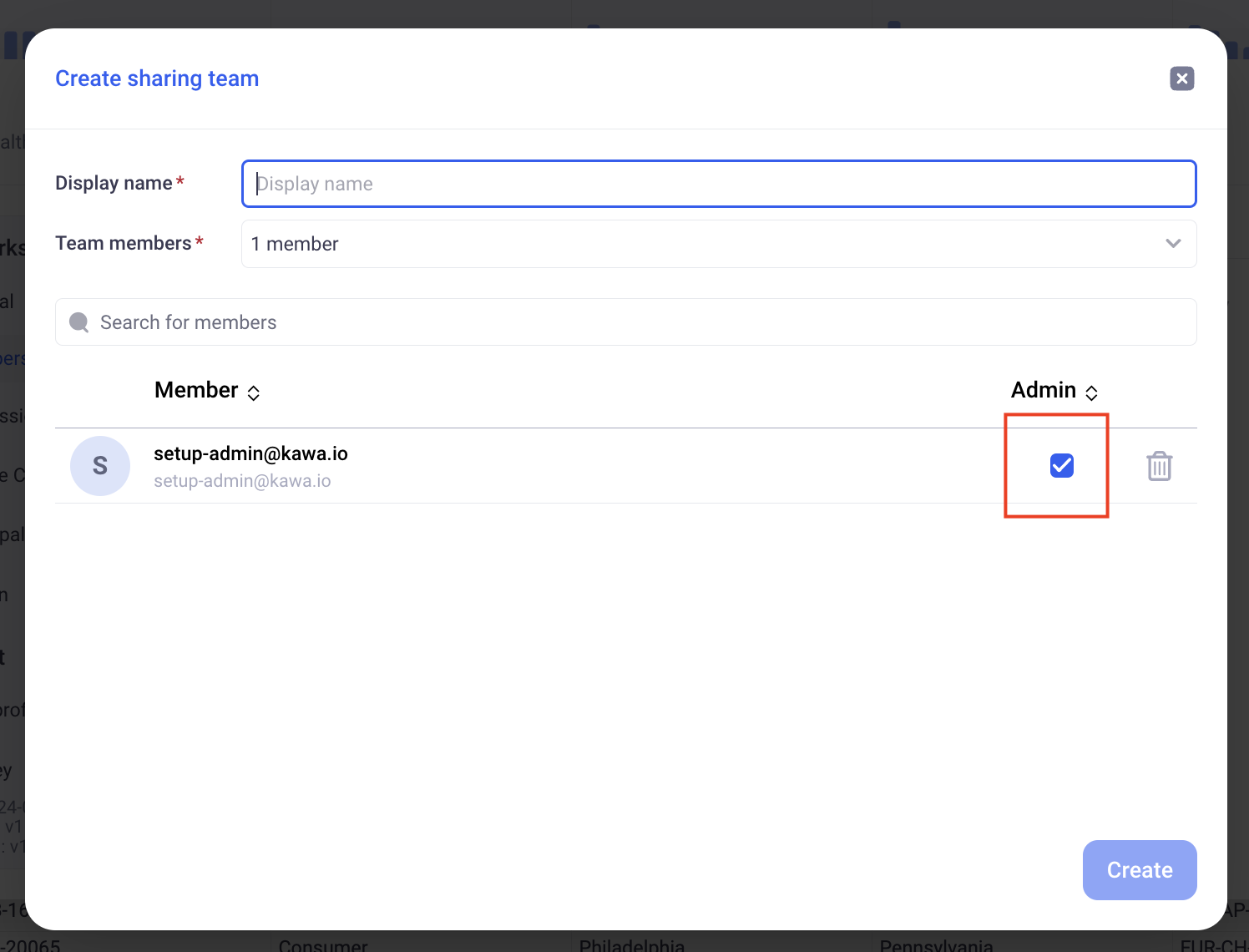
1.4 Teams
Within each workspace, users can be grouped in Teams. See definitions in Terminology section. Teams can be used to share entities with user groups, such as applications, dashboards, sheets and data sources.
Teams are configured on the GUI, from the settings menu.
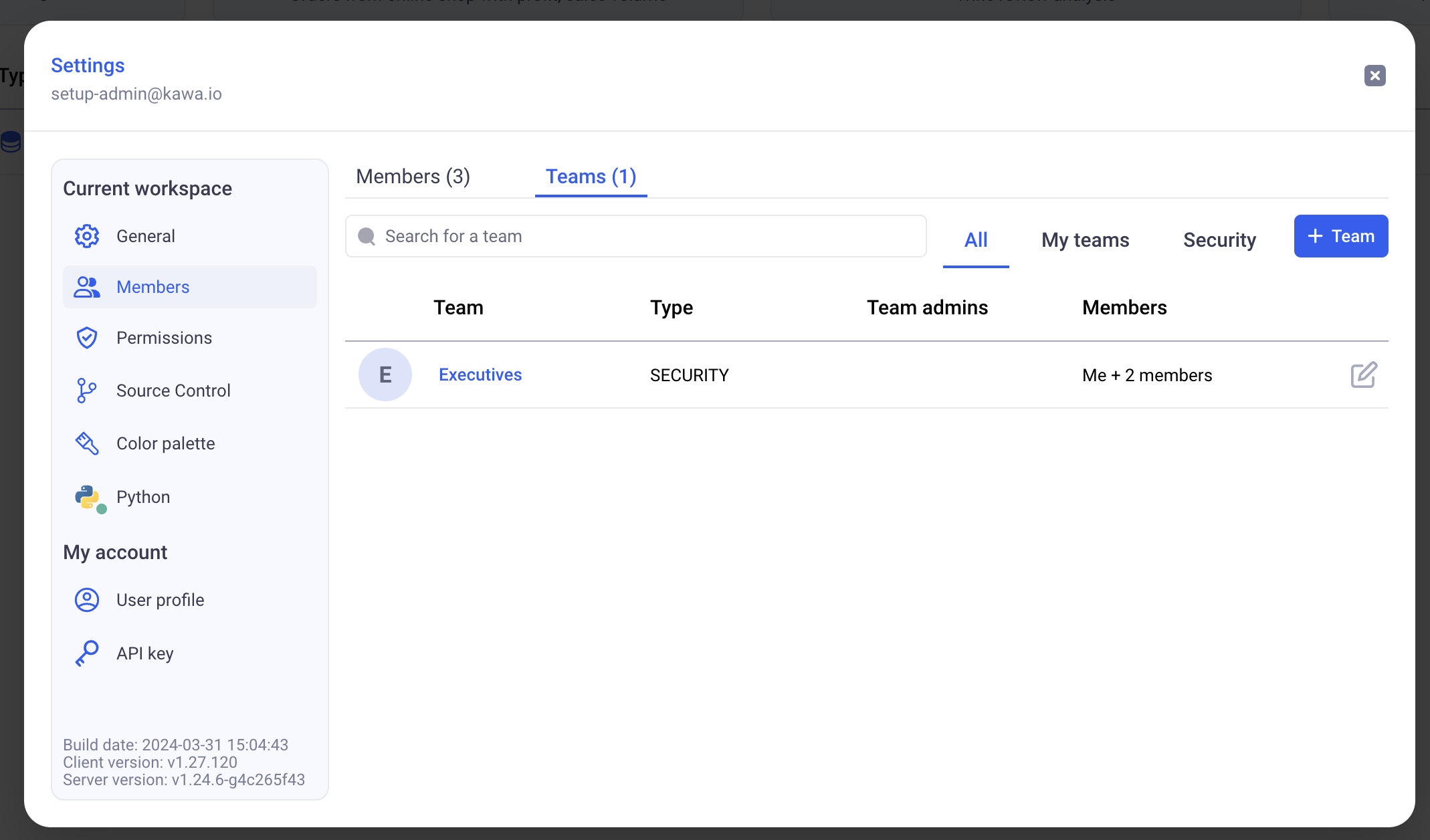
There are two types of teams:
- Sharing teams: Those teams are mainly used to share objects between users.
- Security teams: They work exactly as sharing teams with an additional property: a
security name. Those are used in row level security and column security configuration policies.
1.4.1 Designating team administrators
When adding members to teams, you can designate them as team administrators. Team administrators do NOT need any specific privileges to manage the members of the teams they administrate.
2. Sharing
The main assets of KAWA can be shared across the workspace to which they belong. Sharing allows to set up publishing and collaborating flows between members of the KAWA workspaces.
No information contained in Sheets or Dashboards is confidential, those are mere configuration objects. The security in KAWA only stems from two sources:
- Workspace isolation
- Data ROW and COLUMN level security.
All entities consuming the data (Sheets, Dashboards, Python computations) are without exception subject to the configured RLS and CLS policies.
Important: Entities can not be shared across workspaces.
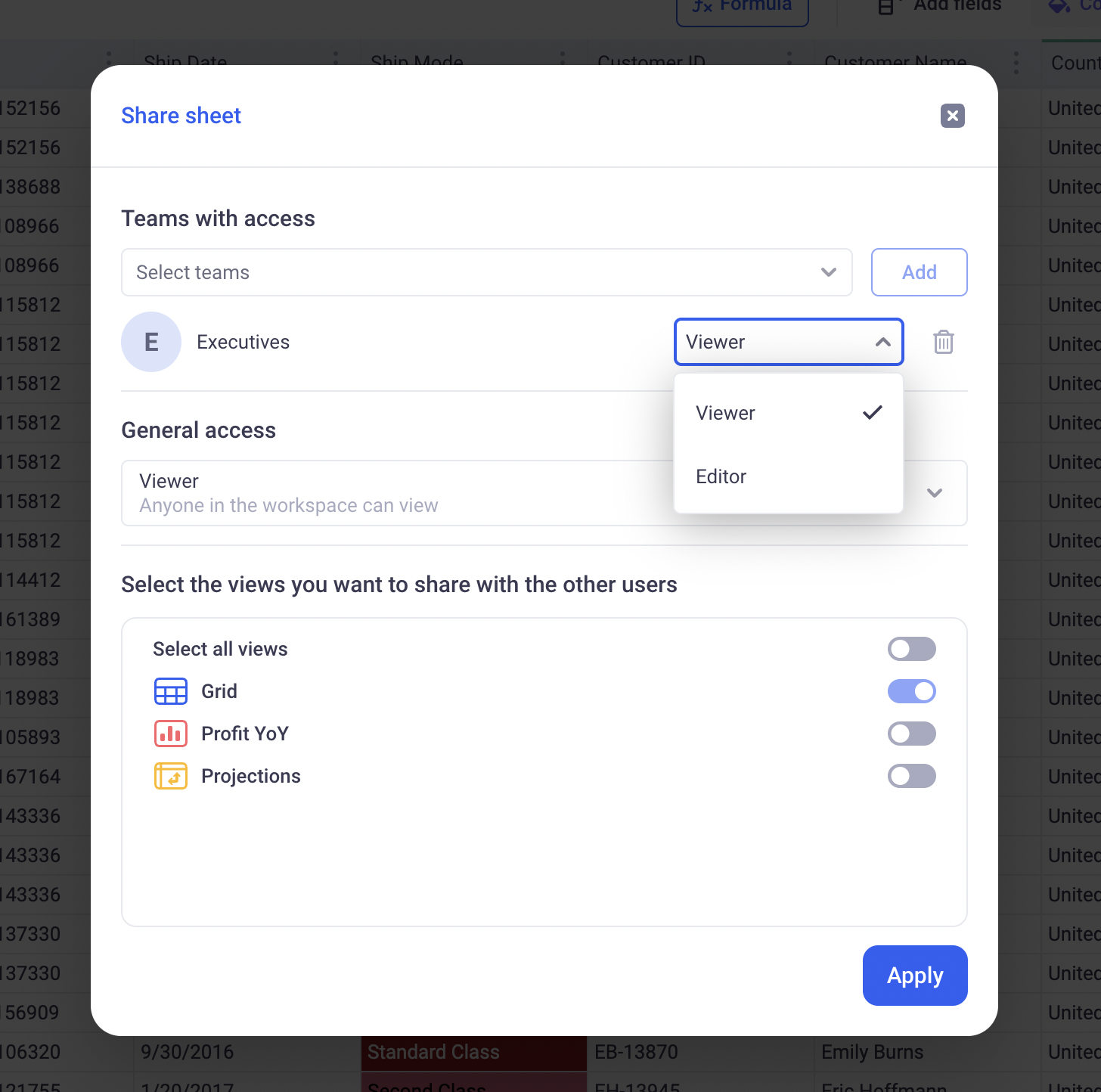
Sharing options:
Entities can be shared with particular teams or with all the users who can access the workspace. When sharing an entity:
- Set a general access policy:
RESTRICTEDmeans users of the workspace cannot access the entityVIEWERmeans that users of the workspace can access the entity but cannot publish any change on it -EDITORthis level means that all the users of the workspace can publish changes on the entity
- Set a per team access policy: The same levels apply.
Important: A user affected by more than one policy will benefit from the higher available access. If a user is targeted by
RESTRICTED,VIEWERandEDITORsimultaneously (through different teams perhaps), they will have theEDITORpolicy on that entity.
2.1 Sharing Sheets and Views
A Sheet contains multiple views, such as charts, grids and pivot tables. They also contain the business logic, expressed through formulas and python scripts.
a. Sheets and Views
A sheet can be shared in Read or Write mode with other users or teams of the workspace.
Within a sheet, views can be shared or private. When a view is shared, it inherits the sharing mode (Read or Write) from its parent sheet.
If a sheet is shared with TeamA for Write, then all the shared views within that sheet will be editable by members of TeamA.
In order to configure sharing parameters for a sheet, use the icon at the top right.
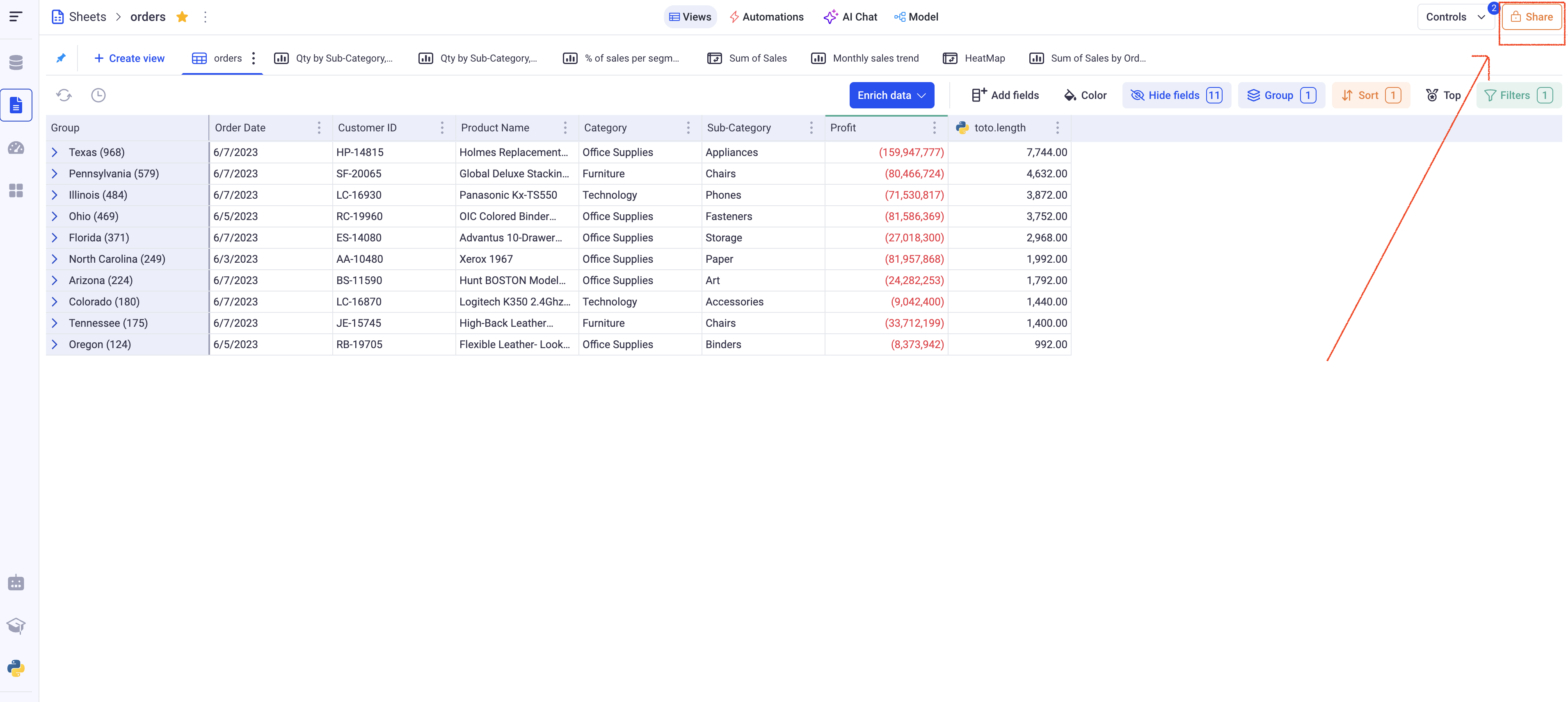
Information: You can also individually share views, either from the sheet sharing parameters, or from the option menu within each individual view.
Note about views:
When views are shared, a control becomes available on them. It lets users rollback to the latest published version, publish a new version (if the user has write permission on the view) or save the view as a new object.
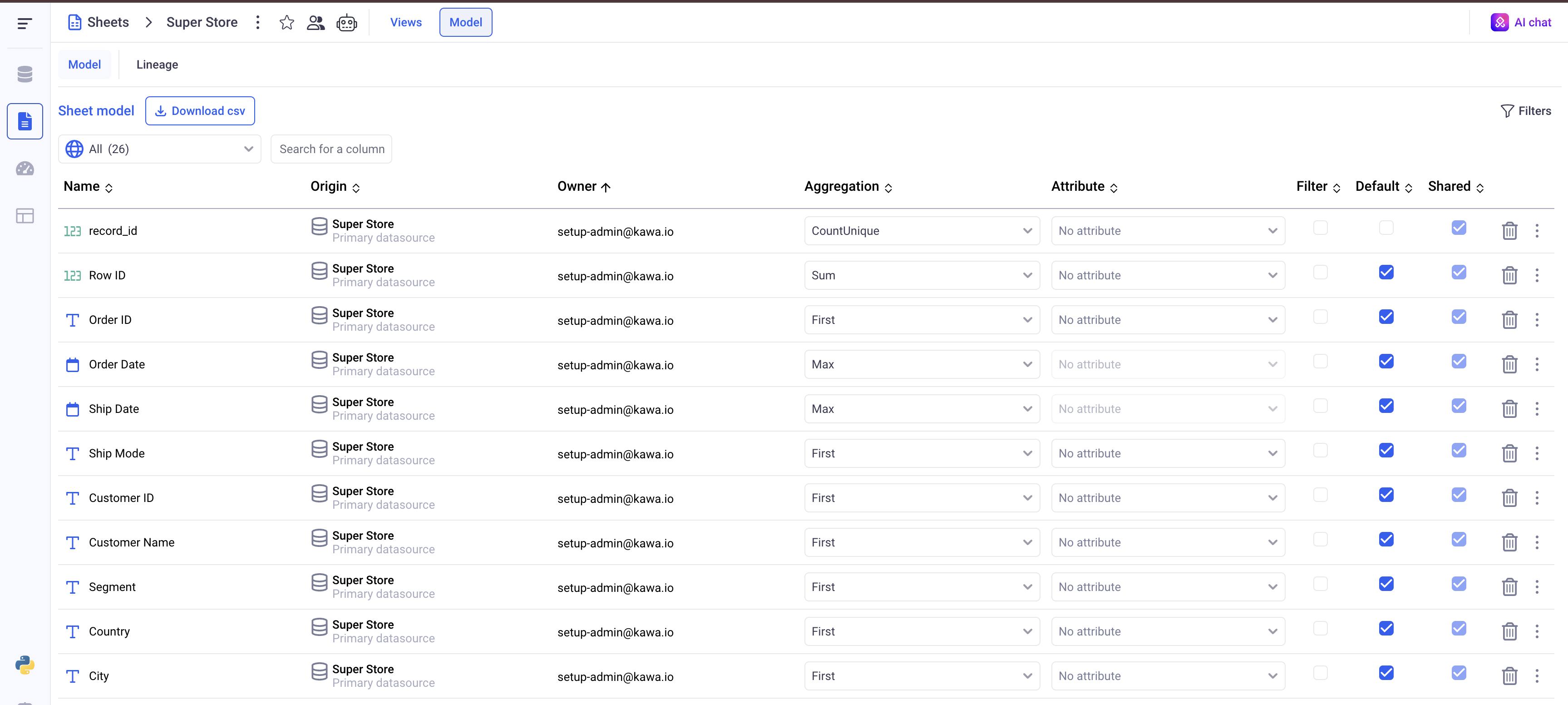
b. Columns: Formulas, Links, Mappings, Python
Within sheets, you can share your columns:
- Formulas,
- Mappings,
- Linked columns,
- Python columns.
This can be done through the sheet model, using the shared checkbox.
Sharing columns will make them available to all users accessing the sheet. They will be able to use those shared columns within their own formulas, and add them to their views - grids, pivots and charts.
2.2 Sharing Data Sources
a. Data Sources
Data Sources can be shared like sheets, within the application.
Important: If a data source is shared with some users, those users might NOT see it if the row level security (RLS) configuration is set to DENY ALL. Make sure to either upload some specific RLS rules or set the general access to ALLOW ALL.
When a data source is shared with writing permissions, users can configure them and manually override data.
In order for a user to be able to configure row level and column security on a data sources, two conditions must be met:
- The user must be able to edit the data source (shared with writing permissions)
- The user must have the
Manage Data Source Securityflag enabled.
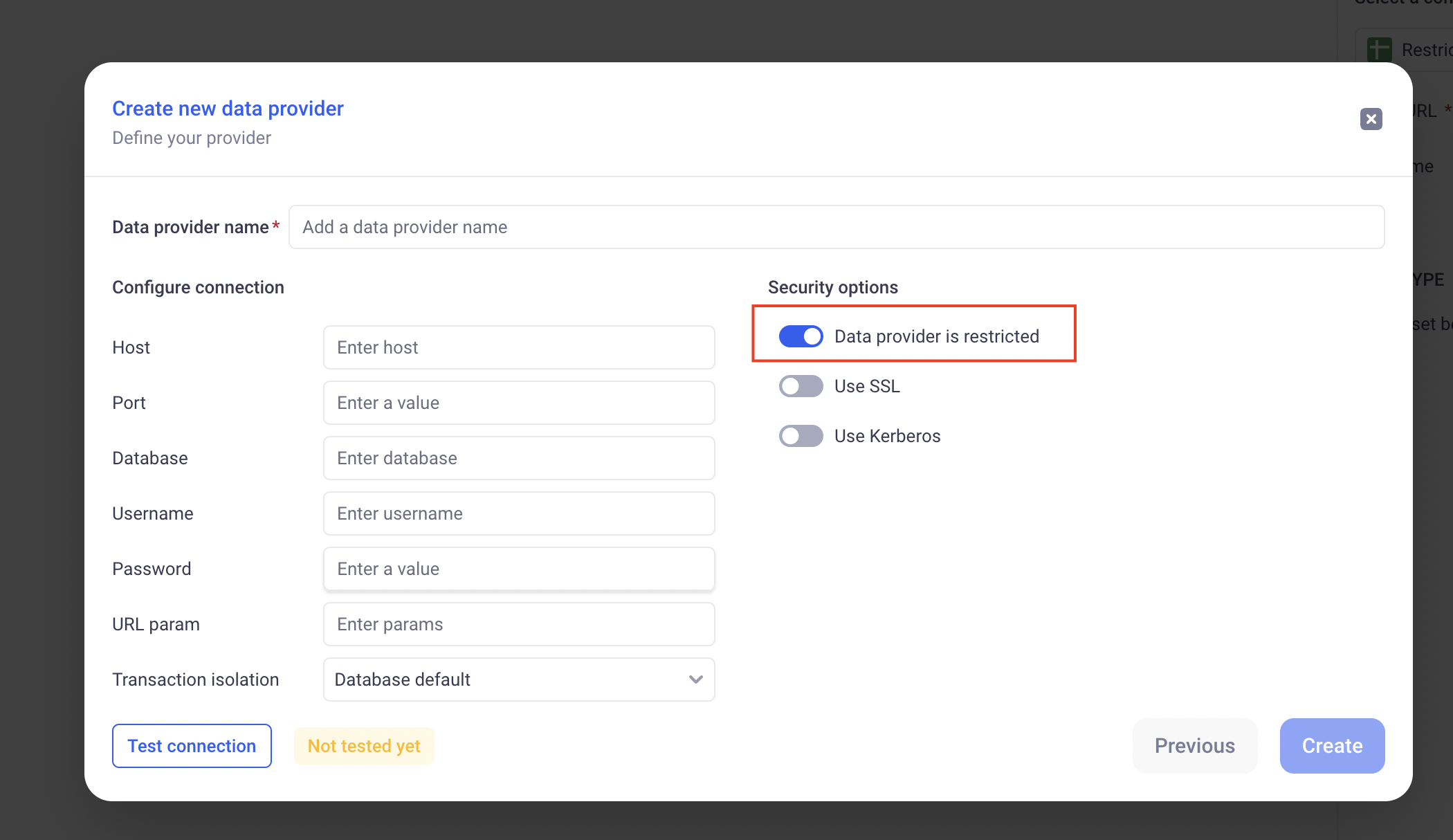
b. Data Providers
Data providers are databases or external APIs to which KAWA is connected to import data. When a data provider is restricted, only users with the Access restricted data and restricted data providers flag can access them to create new data sources.
2.3 Sharing Dashboards
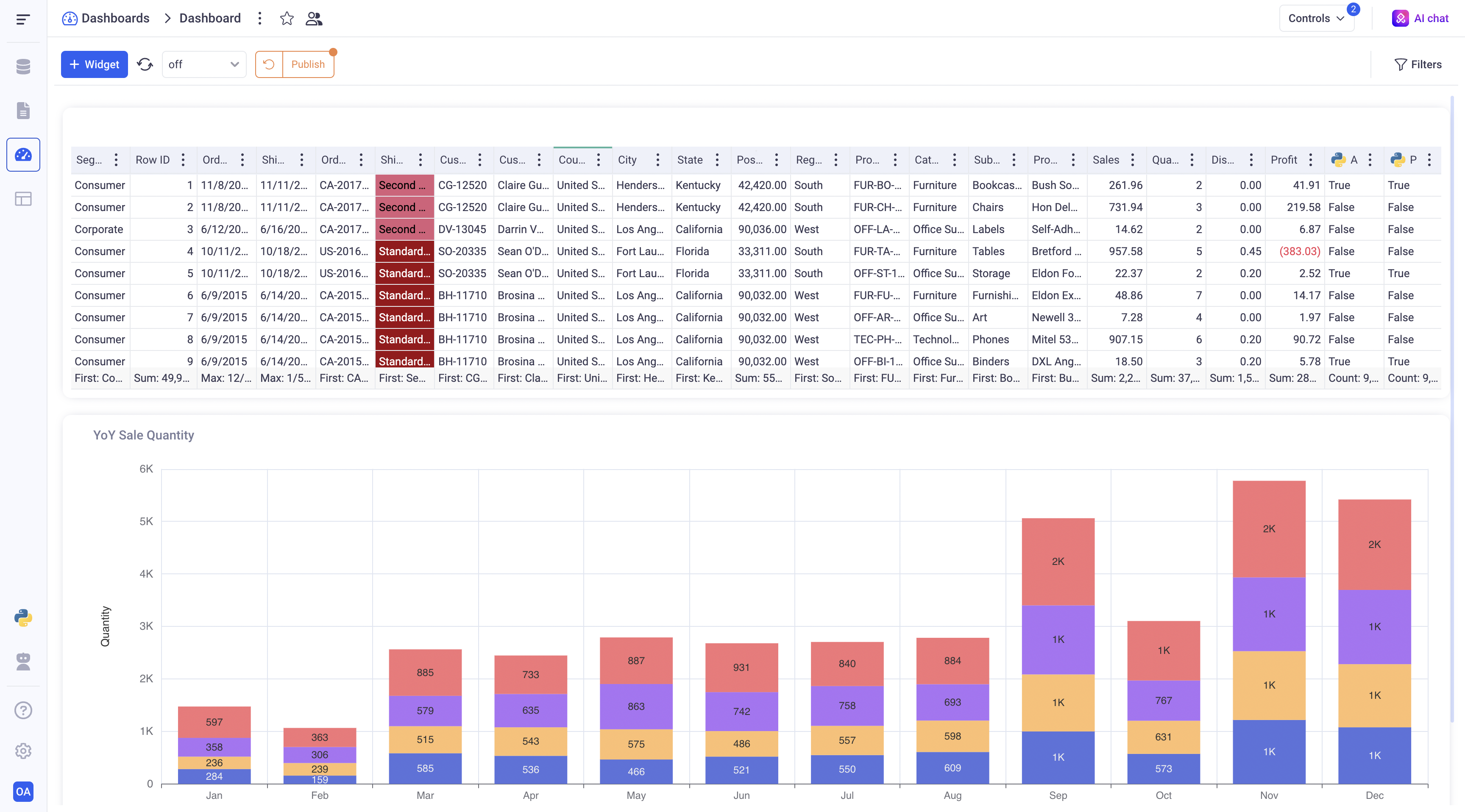
Dashboards can be shared in the UI, in the same way as sheets and data sources. All the widgets of the dashboards follow the dashboard sharing policies and publications.
It means that the PUBLISH and ROLLBACK buttons on the dashboard will affect all views of the dashboards automatically.
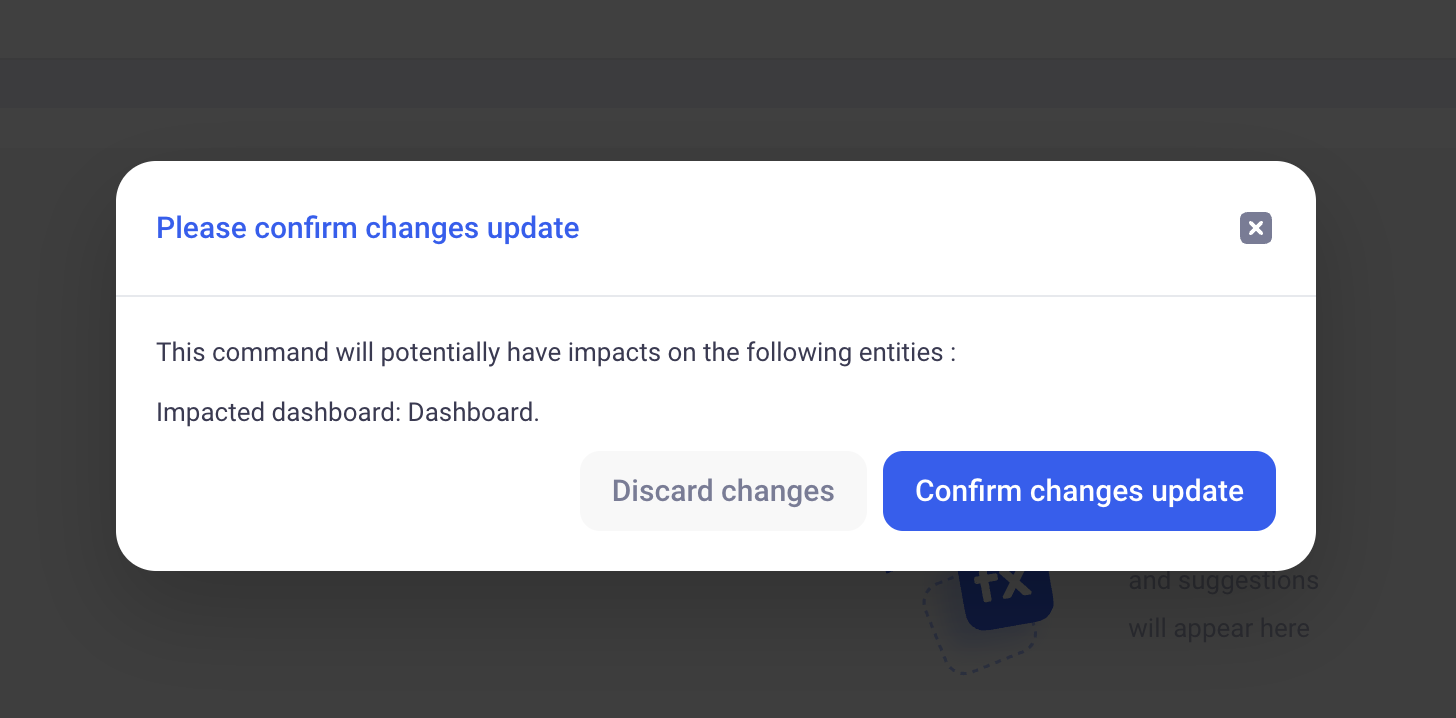
When sheets are used in shared dashboards, modifying elements of their model (like formulas for example), will result in a warning for the users:
2.4 Sharing Apps
Applications can be shared in the UI, in the same way as sheets and data sources. All the pages of the apps follow the zpp sharing policies and publications.
It means that the PUBLISH and ROLLBACK buttons on the app will affect all pages (views, dashboards) of the app automatically.
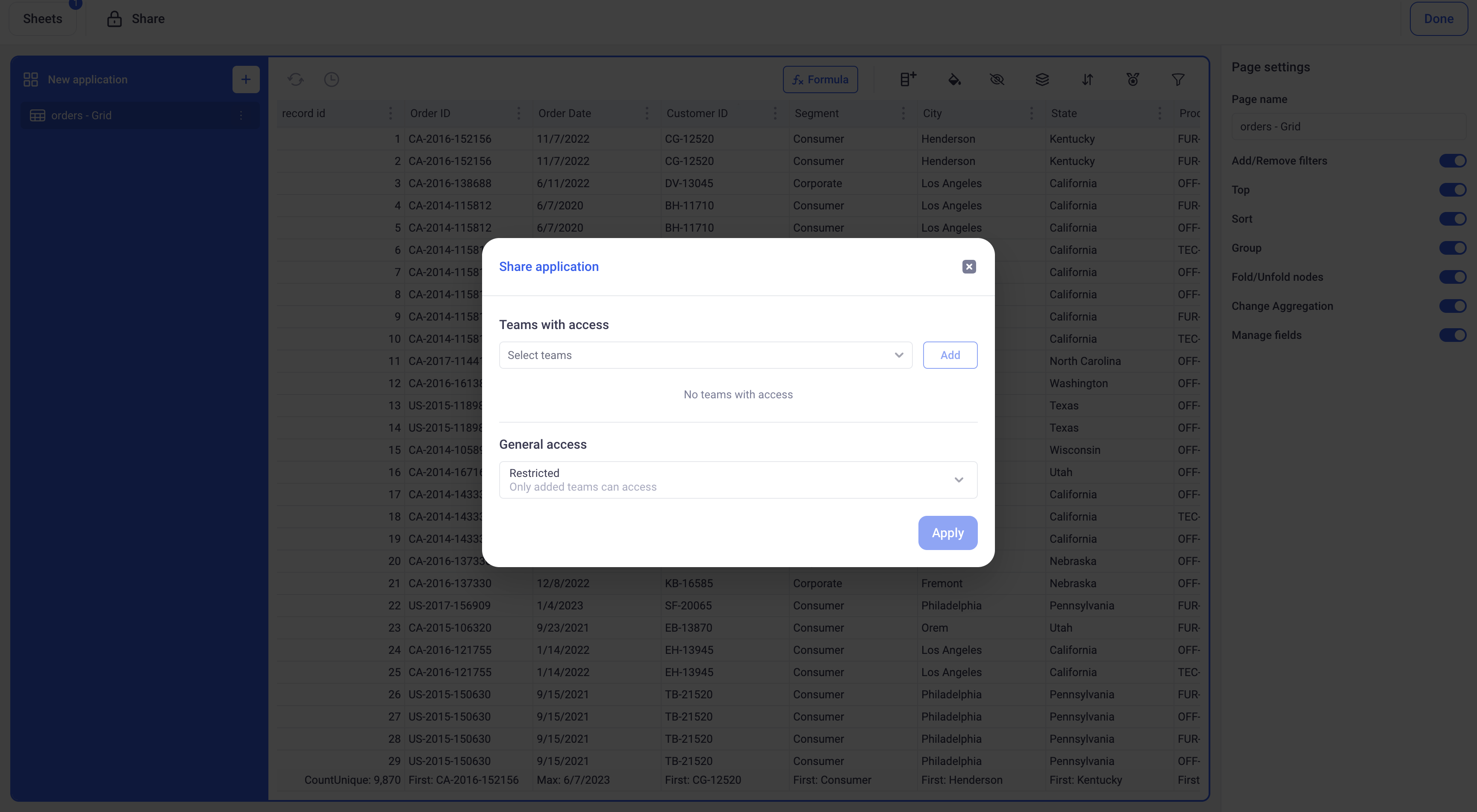
When sheets are used in shared apps, modifying elements of their model (like formulas for example), will result in a warning for the users.
2.5 Sharing Knowledge
As with the other entities, Knowledge can be shared in the workspace. When a user does not have read access to a knowledge, they will not be able to access the content of the knowledge anywhere. (Parsed data, previews etc)
2.5 Sharing Workflows
Workflows can be shared in the workspace in the same way as the other entities.
If a user does not have the required permission on a sheet that is used in a workflow, they cannot modify elements of their model. In this case the workflow editor will show an error, and the update of the view will not be applied until a user with the appropriate permissions modifies the workflow or grants the missing access.
