Snowflake native connection
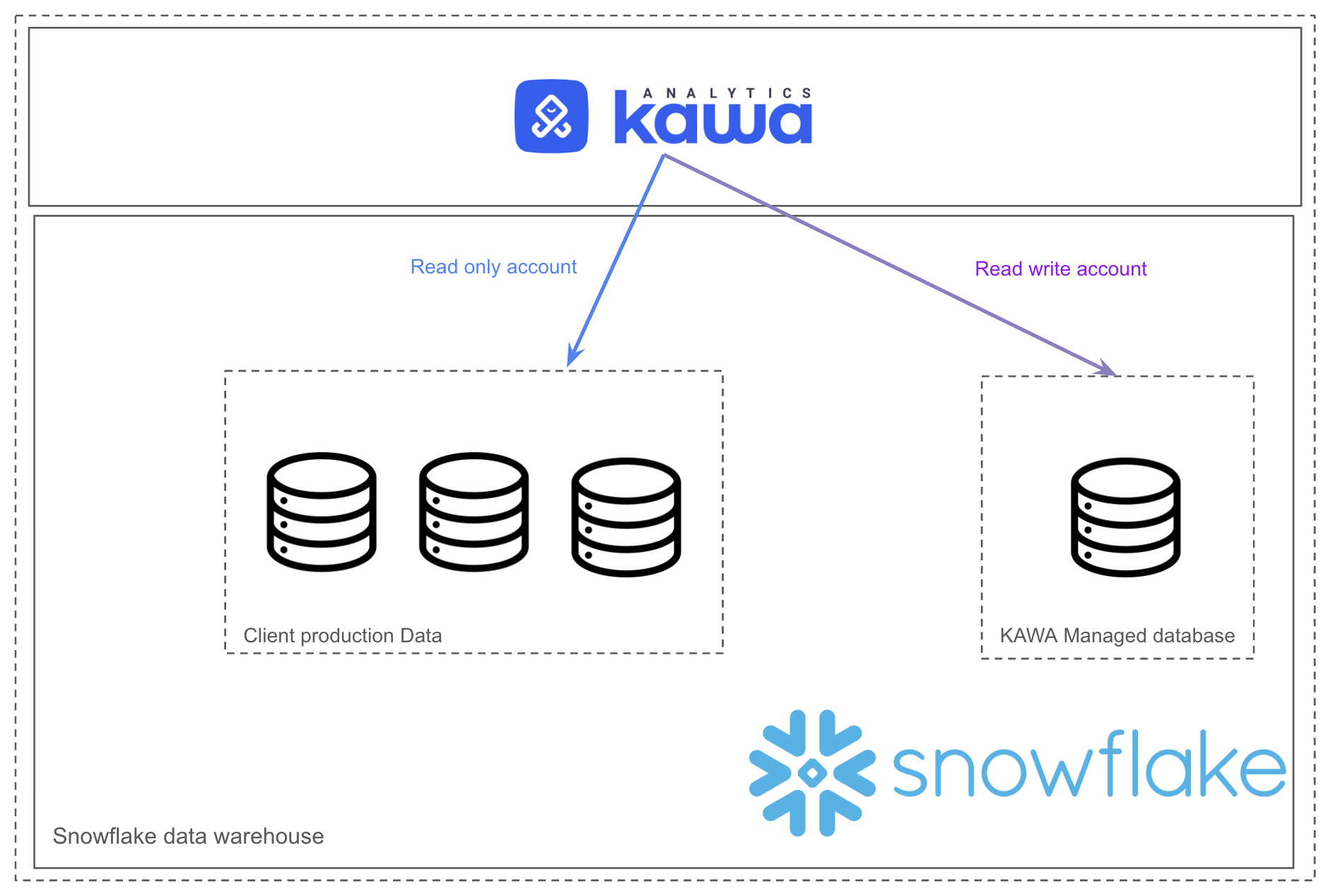
This section illustrates how KAWA can leverage Snowflake as its data warehouse.
1. Overview
KAWA integrates natively with Snowflake as a primary data warehouse, enabling seamless connectivity to your centralized enterprise datasets. By leveraging Snowflake’s scalable compute and elastic storage architecture, KAWA empowers users to explore, transform, and visualize data through its intuitive analytics interface—while maintaining full SQL compatibility and direct access to live Snowflake tables. This integration unlocks powerful capabilities such as Python-based ETL, dynamic schema augmentation, and real-time insights, all orchestrated within the Snowflake ecosystem. With KAWA, organizations can unify interactive analytics and advanced data workflows on Snowflake, combining performance, governance, and usability in one streamlined platform.
2. Configuration guide
This configuration guide outlines how to connect KAWA to a snowflake data warehouse.
2.1 Configuring Snowflake
Connect to your snowflake instance with a user that can create databases, roles and users.
a. Creating a database and schema for KAWA to write in
KAWA will create tables containing user data such as CSV uploads, pandas data frames etc.. in this database and schema.
CREATE DATABASE KAWA_ANALYTICS_DB
COMMENT = 'Database for KAWA to write back its objects';
CREATE SCHEMA KAWA_ANALYTICS_DB.KAWA;
b. Create a role and a user with all permissions in the new schema
This creates a role with Write Back capabilities in the kawa database and schema.
CREATE ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
-- Grand access to a warehouse
GRANT USAGE ON WAREHOUSE compute_wh TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
-- Access to the DB and schema
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE KAWA_ANALYTICS_DB TO ROLE KAWA_WRITE_BACK_ROLE;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
-- Allow to create objects
GRANT CREATE TABLE ON SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
GRANT CREATE VIEW ON SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
GRANT CREATE STAGE ON SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
-- All privileges on current objects
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL VIEWS IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
-- All privileges on future objects
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON FUTURE TABLES IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON FUTURE VIEWS IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON FUTURE SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_write_back_role;
Create a user associated with that role:
-- KAWA Write back user
CREATE USER kawa_write_back_user
PASSWORD = '@StrongPassword@'
DEFAULT_ROLE = kawa_write_back_role
DEFAULT_WAREHOUSE = compute_wh
COMMENT = 'User with full access to kawa_analytics_db only';
GRANT ROLE kawa_write_back_role TO USER kawa_write_back_user;
c. Create a role / user with readonly access on selected databases
The readonly user must have permission to read the kawa_analytics_db created in the previous steps. It must also be able to access all the schemas and databases (SELECT only) that you want to connect to KAWA.
Make also sure that this user can create views in the KAWA database and schema.
CREATE ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
-- Grand access to a warehouse
GRANT USAGE ON WAREHOUSE compute_wh TO ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
-- 🚨 Specific for the kawa schema
GRANT CREATE VIEW ON SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
-- Grant read on kawa_analytics_db.kawa for all tables and views
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE kawa_analytics_db TO ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL VIEWS IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
GRANT SELECT ON FUTURE TABLES IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
GRANT SELECT ON FUTURE VIEWS IN SCHEMA kawa_analytics_db.kawa TO ROLE kawa_readonly_role;
-- Add all the necessary USAGE and SELECT grants to all the
-- databases and schemas that you want to connect to KAWA.
-- 🚨 DO NOT GRANT ANY OTHER PERMISSIONS BESIDES SELECT and USAGE to this role.
Now, create a user with the new readonly role.
-- KAWA readonly user
CREATE USER kawa_readonly_user
PASSWORD = '@StrongPassword@'
DEFAULT_ROLE = kawa_readonly_role
DEFAULT_WAREHOUSE = compute_wh
COMMENT = 'Readonly KAWA user';
GRANT ROLE kawa_readonly_role TO USER kawa_readonly_user;
Alternatively, you can opt to configure a RSA keypair to authenticate your users. In oder to do so, for each user:
1) Generate a private key with:
# Key has to be in the PKCS8 format (Starting with: -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----)
openssl genrsa -out rsa_key.pem 2048
2) Derive your public key from the private key:
openssl rsa -in rsa_key.pem -pubout -out rsa_key.pub
3) Configure your users
-- Extract the base64 part from your public key
ALTER USER kawa_readonly_user
SET RSA_PUBLIC_KEY='MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAkm.....9QIDAQA';
2.2 Configuring KAWA
KAWA needs the following environment variables to work with this setup:
# Common: Warehouse and account
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT=ACCOUNT1
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE=compute_wh
# configure the readonly user (do not use password if using a private key)
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD=@StrongPassword@
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_USER=kawa_readonly_user
# Configure the write back user (do not use password if using a private key)
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_WRITER_CATALOG=KAWA_ANALYTICS_DB
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_WRITER_PASSWORD=@StrongPassword@
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_WRITER_SCHEMA=KAWA
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_WRITER_TABLE_PREFIX=KW__
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_WRITER_USER=kawa_write_back_user
If you opted for the keypair authentication method, set the following two variables instead of the passwords:
# The private key files should be accessible from the Java instance
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_PATH_TO_PRIVATE_KEY="/path/to/private/key/for/readonly/user"
KAWA_SNOWFLAKE_WRITER_PATH_TO_PRIVATE_KEY="/path/to/private/key/for/writeback/user"
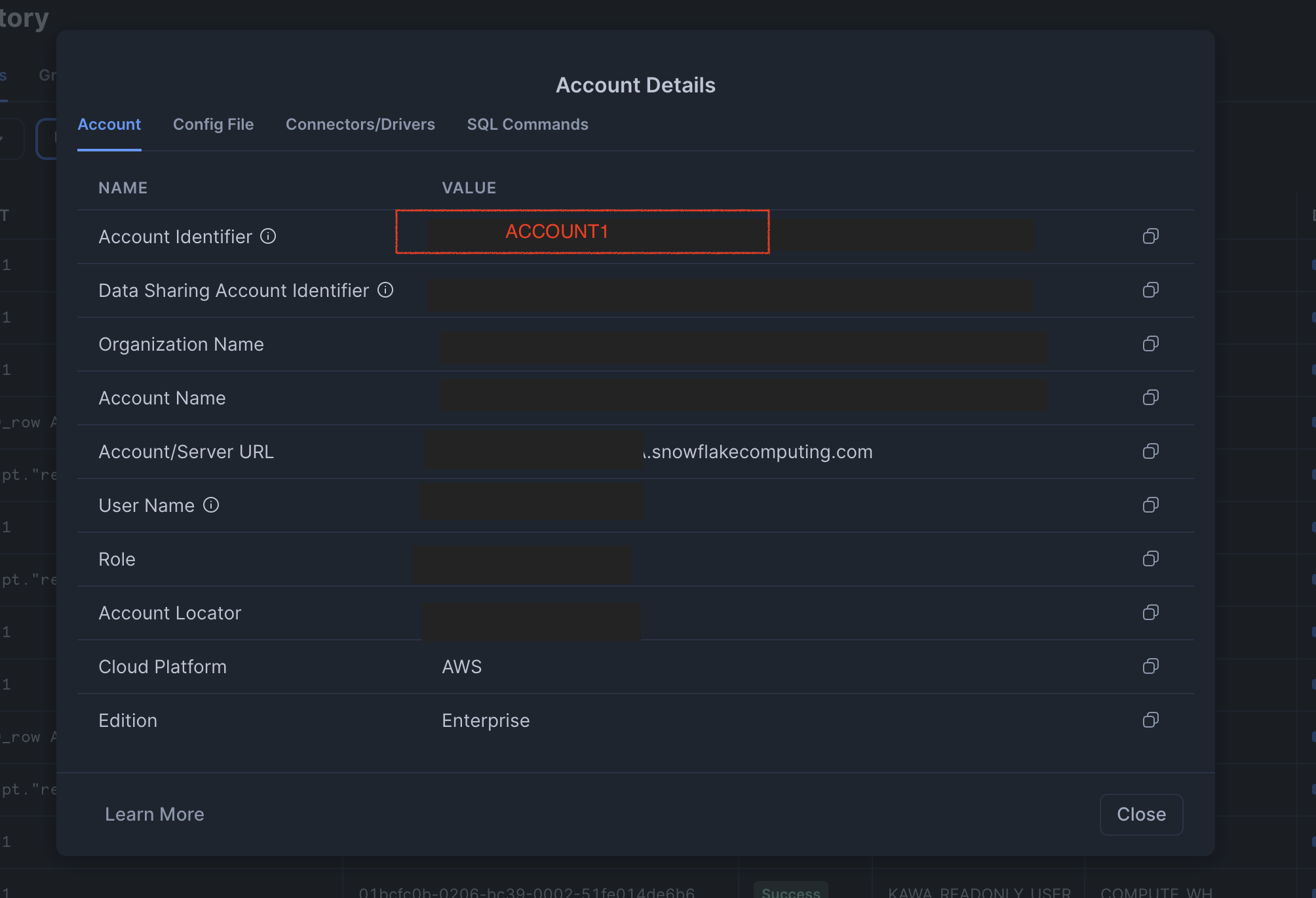
In the snowflake GUI, you can easily retrieve your account identifier.